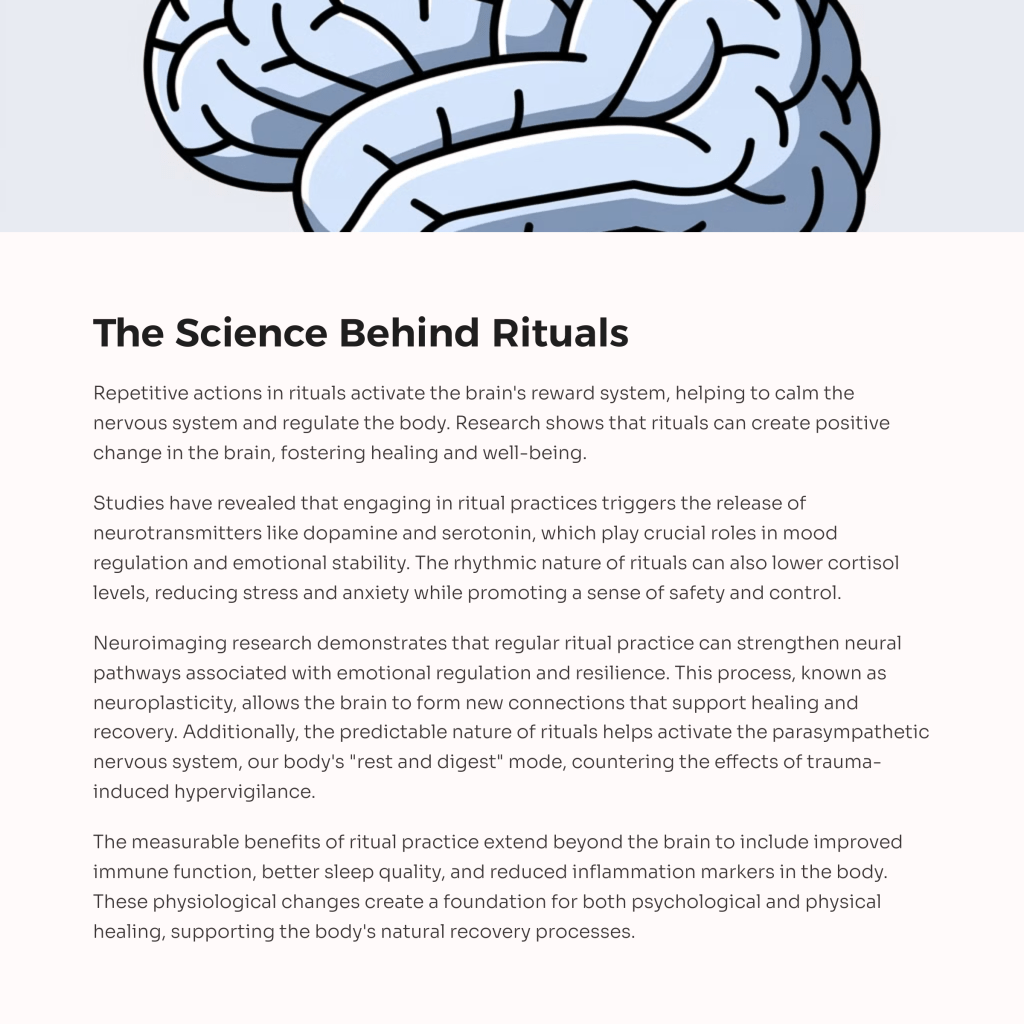
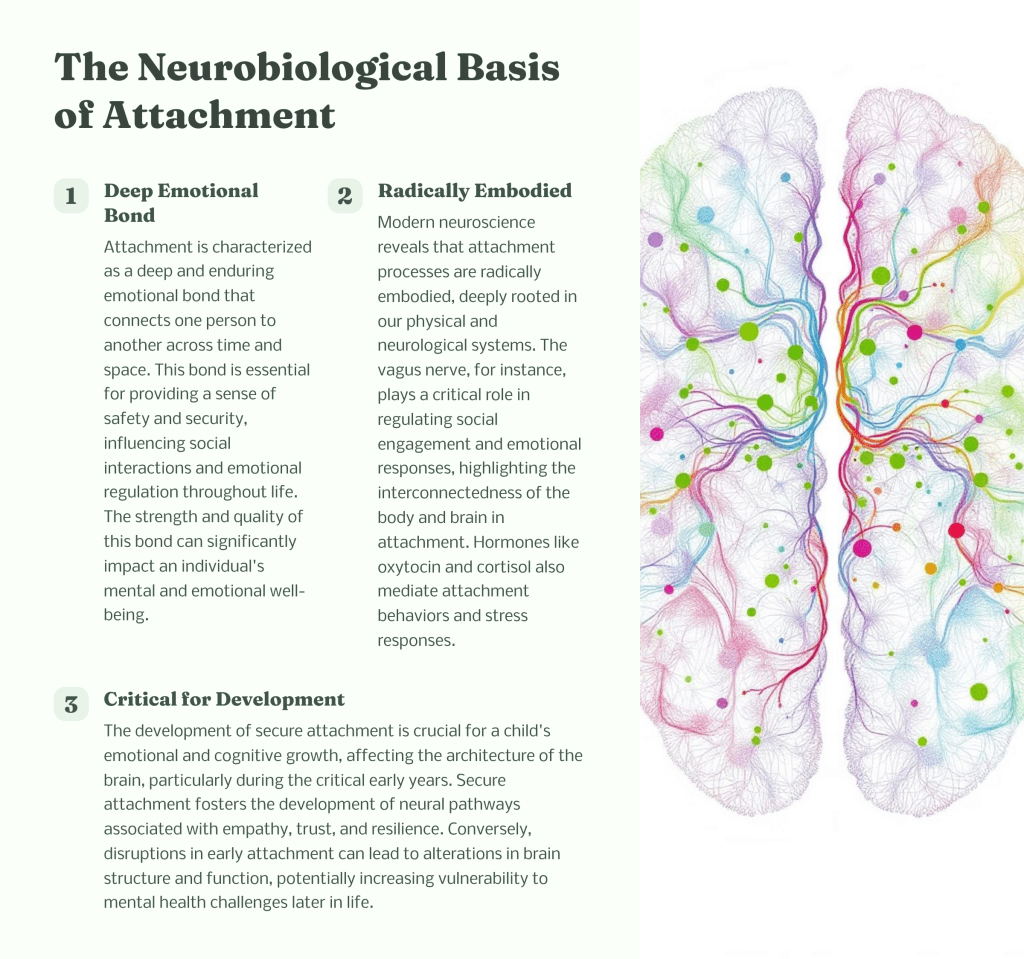
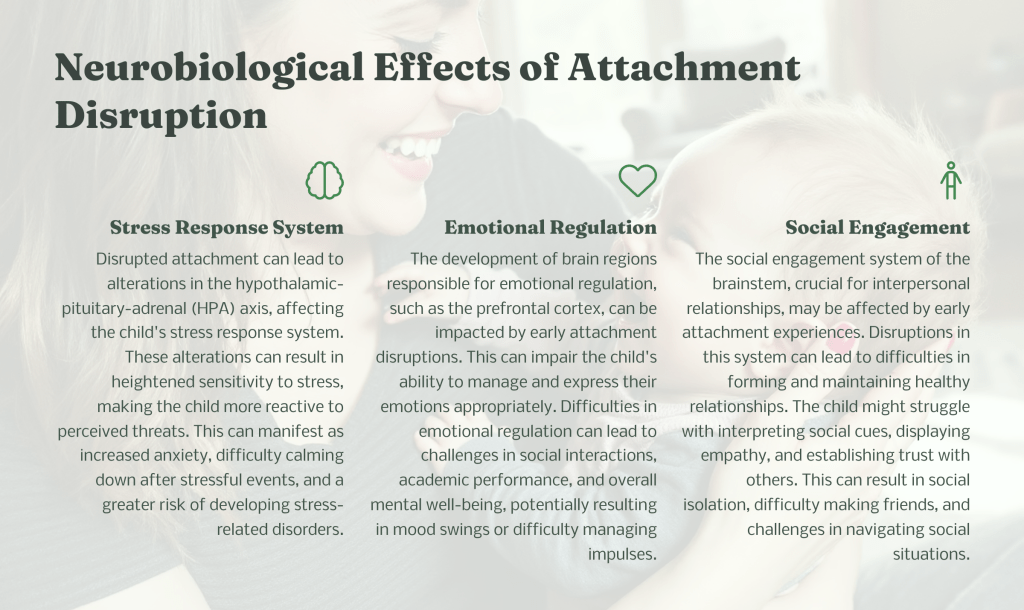
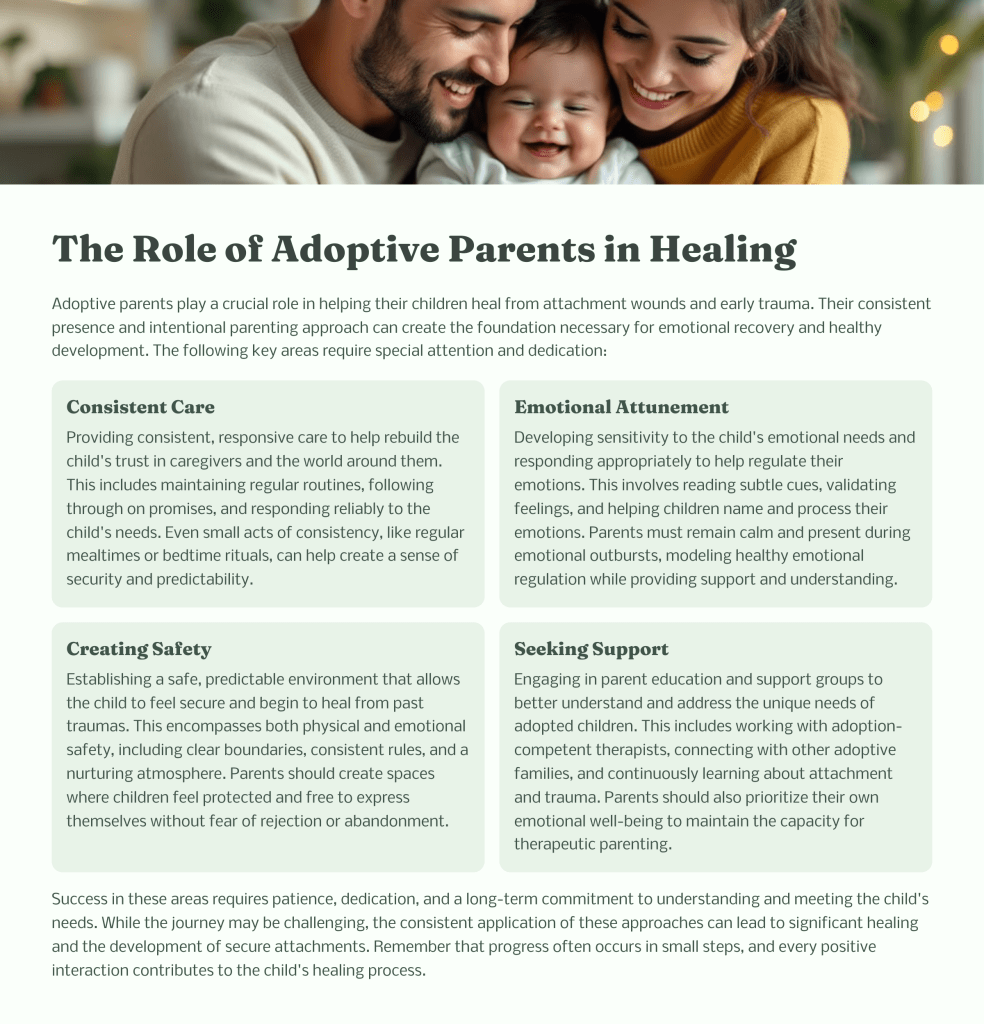
Why Trauma-Informed Care Matters—and How to Stay Equipped as a Trauma Champion
Trauma affects more people than we realize. Whether in schools, healthcare, workplaces, or communities, the need for trauma-informed care has never been greater. Professionals on the frontlines—therapists, teachers, social workers, leaders, and advocates—are increasingly recognizing that understanding trauma is not optional; it’s essential.
But here’s the challenge: staying current with trauma-informed best practices can feel overwhelming. New research, new strategies, and new demands necessitate ongoing resources to remain effective and avoid burnout. That’s precisely why I created the Trauma Champions Newsletter.
What Is Trauma-Informed Care?
At its core, trauma-informed care is an approach that:
- Recognizes the widespread impact of trauma
- Identifies the signs and symptoms in individuals, families, and organizations
- Responds with policies, practices, and programs that foster safety and healing
- Prevents re-traumatization, ensuring care is supportive and empowering
This approach matters because trauma doesn’t just affect individuals—it ripples across families, schools, workplaces, and entire communities. When professionals are equipped with trauma-informed strategies, they don’t just treat symptoms; they create conditions for long-term resilience and growth.
Introducing the Trauma Champions Newsletter
The Trauma Champions Newsletter is my way of making trauma-informed care practical, accessible, and sustainable for busy professionals.
Each issue includes:
- Practical strategies you can apply immediately in clinical, educational, and community settings
- Insights on the latest trauma-informed care research and methods
- Tools for preventing burnout and compassion fatigue
- Resources to help leaders and organizations build trauma-sensitive cultures
Thousands of professionals worldwide have already participated in my training and certification programs. This newsletter brings that same expertise straight to your inbox.
👉 Subscribe free today at TraumaChampions.com
Why Join?
By subscribing, you’ll not only stay up to date—you’ll join a growing movement of Trauma Champions committed to transforming care. Together, we’re working to:
- Make trauma-informed care the standard across schools, agencies, and organizations
- Provide families with hope and healing tools
- Build stronger, more resilient communities
If you’re passionate about trauma-informed practice, this is your space to grow, connect, and lead.
Take the Next Step
Don’t miss out on tools, training, and encouragement designed to help you thrive in this critical work.
👉 Sign up now at TraumaChampions.com and start receiving trauma-informed insights directly in your inbox.
Together, we can turn trauma into resilience—and create real change.