The Hidden Messages in Your Discomfort: Why Processing Emotions is Your Path to Freedom
You know that feeling—a nagging unease in your stomach, a restlessness you can’t quite name, or a vague sense that something isn’t right even when everything looks fine on the surface. Most of us try to push these feelings away, distract ourselves with work, social media, or other activities. But what if these uncomfortable sensations aren’t problems to be solved, but messengers trying to deliver critical information?
The Weight of Unfinished Emotional Business
That persistent discomfort you’re experiencing might not be a warning about what’s coming—it could be an echo from your past that’s been quietly traveling with you. Unprocessed emotions don’t simply disappear because we ignore them. They settle into our bodies and minds like uninvited houseguests, taking up space and influencing how we move through the world.
Think of these unresolved feelings as unopened letters from earlier versions of yourself. Some contain wisdom and insights that could guide you forward. Others are simply remnants from chapters of your life that have already ended but haven’t been adequately acknowledged or grieved. All of them represent parts of you that are still waiting to be heard and integrated.
These emotional fragments aren’t trying to torture you—they’re signals pointing toward aspects of yourself that haven’t been fully understood or accepted. They’re like a persistent knock at the door from the parts of you that remain unfree, asking for attention and care.
Creating Space for Healing
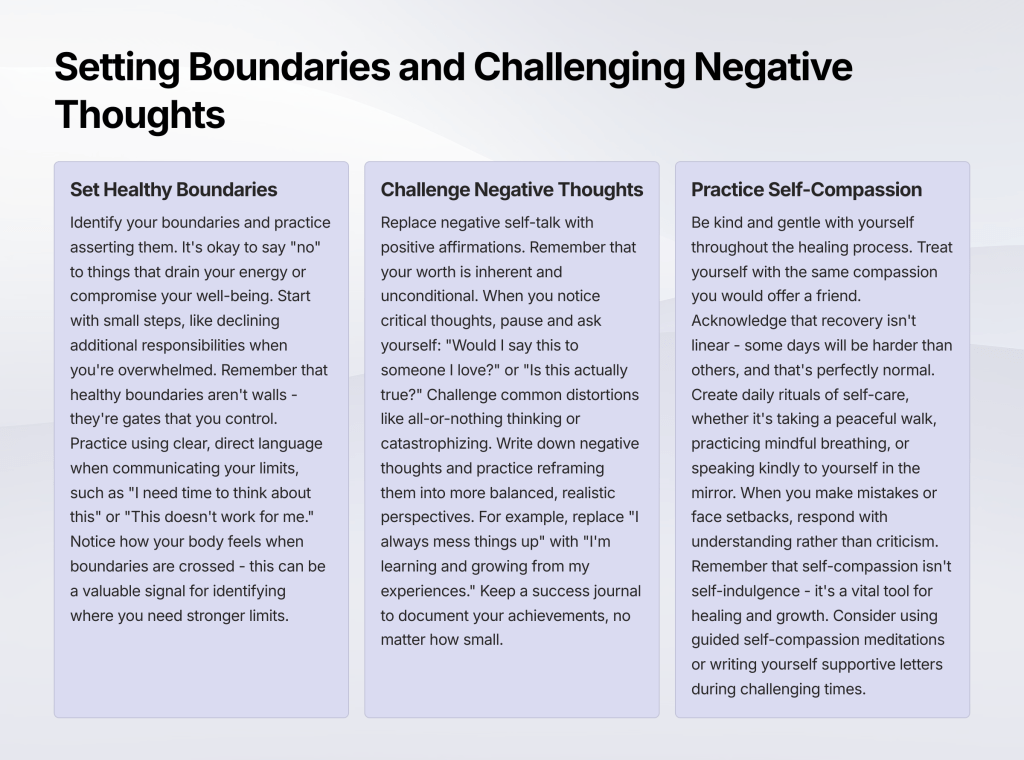
When you’re ready to stop running from these feelings and start listening to them, the process begins with creating a sense of safety. This means finding physical and emotional spaces where you can turn toward your discomfort rather than away from it. It’s about developing the courage to ask, “What are you trying to tell me?”
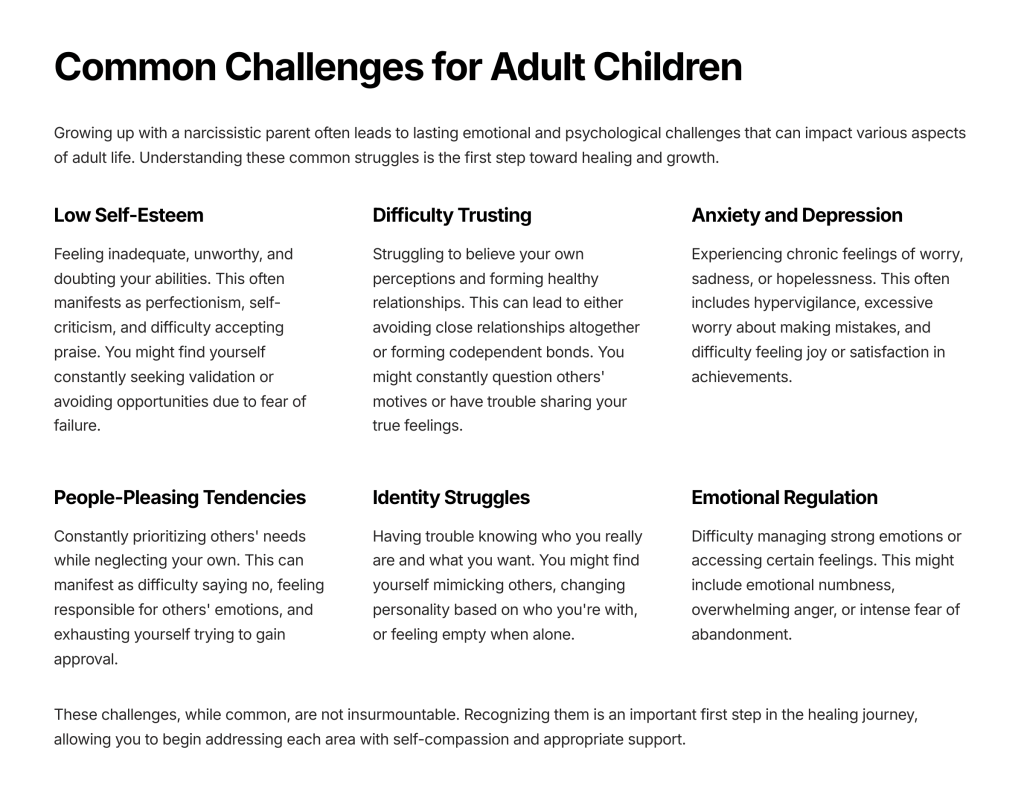
This journey often brings up forgotten memories and long-buried emotions. You might suddenly remember moments from childhood that shaped how you see yourself, or realize that specific triggers—anger, sadness, anxiety—have been trying to wake you up to unmet needs or unacknowledged pain.
The healing process isn’t always gentle. It might involve crying for losses you never properly mourned, revisiting difficult memories to offer your younger self the comfort or voice they never had, or simply sitting with emotions you’ve spent years avoiding. But as you move through this process, something remarkable happens: you begin to feel lighter, as if you’re literally releasing weight you didn’t realize you’d been carrying.
Your body, too, holds onto emotional experiences. Physical practices such as exercise, stretching, or allowing yourself to shake or tremble can help release stored tension and trauma. Sometimes the body knows how to let go in ways the mind hasn’t figured out yet.
The goal isn’t to eliminate all discomfort from your life, but to learn how to be present with your feelings as they arise. When you can face what’s wrong without immediately trying to fix or escape it, you begin to uncover parts of yourself that have been buried under layers of personas, beliefs, and protective strategies.
You were never actually lost—just hidden. The discomfort was your authentic self’s way of reminding you that it was still there, waiting to be reclaimed.
Discomfort as Your Growth Partner
Here’s something our culture rarely teaches us: discomfort is often the seed of positive change. Most transformations begin not with a sudden burst of inspiration but with experiences that initially bring uncertainty, fear, and anxiety. This happens because we’re remarkably good at adapting to situations that aren’t quite right for us, often waiting until crisis forces our hand before we make necessary changes.
Your discomfort isn’t punishment—it’s information. It’s your inner wisdom communicating that something needs to shift, that there’s another way forward even if you can’t see it clearly yet. Think of discomfort as a caring friend who’s willing to tell you brutal truths that others might avoid.
Many people resist this messenger, which is why their lives can feel stuck or repetitive. But learning to sit with discomfort, to let it reveal what it needs to show you, is one of the most valuable skills you can develop. Discomfort, like anger, grief, and jealousy, serves a purpose—it’s trying to guide you toward something meaningful.
The Sneaky Ways We Resist Our Own Growth
Even when we intellectually understand that change would benefit us, our minds have clever ways of keeping us stuck. These psychological patterns often operate below conscious awareness, sabotaging our best intentions:
The Comfort of Familiar Discomfort. Strangely, we often unconsciously sabotage ourselves when life gets too good. If you’re used to struggle or chaos, peace and happiness can feel foreign and threatening. Your mind might create problems or find ways to return to familiar levels of stress, even when that familiar state isn’t pleasant. Change—even positive change—feels uncomfortable until it becomes your new normal.
The Limits of Our Imagination. Our minds are remarkably good at solving problems we’ve encountered before, but they struggle to envision genuinely new possibilities. When contemplating change, we often can only imagine variations of what we’ve already experienced. This limitation can lead us to believe that our current options are more limited than they actually are. Real growth requires accepting uncertainty and exploring unknown territory, which can feel deeply unsettling.
Expecting the Worst. Human brains are wired to notice and remember negative experiences more vividly than positive ones. This survival mechanism once kept our ancestors alive, but now often keeps us playing small. We tend to overestimate the likelihood and severity of bad outcomes while underestimating our ability to handle challenges or create positive change. This negativity bias can make staying in uncomfortable but familiar situations seem safer than taking risks toward something better.
The Sunk Cost Trap. Sometimes we remain committed to jobs, relationships, or life paths that aren’t working simply because we’ve already invested a significant amount of time, energy, or money in them. The thought of “wasting” that investment can keep us trapped in situations that no longer serve us, preventing us from pursuing options that might be much more fulfilling.
First Impressions Stick. Our brains tend to give special weight to early experiences and first impressions, making it harder to see new possibilities later. Suppose you learned early in life that you weren’t good at something, or that specific dreams were unrealistic. In that case, these initial conclusions can overshadow evidence to the contrary that emerges as you grow and change.
Temporary Feelings, Permanent Decisions. When we’re going through difficult emotions or challenging periods, it’s easy to assume these temporary states represent permanent realities. A bad week can feel like a prediction of a bad life. A period of sadness can seem like evidence that happiness isn’t possible. Learning to recognize the temporary nature of most emotional states can prevent us from making major life decisions based on passing feelings.
Insight Without Action. Sometimes, we become so caught up in understanding our patterns and having revelations about ourselves that we forget to actually implement the changes. Self-reflection can become its own form of avoidance when we use it to delay the often mundane, repetitive work of building new habits and sticking to healthier choices.
Living More Intentionally
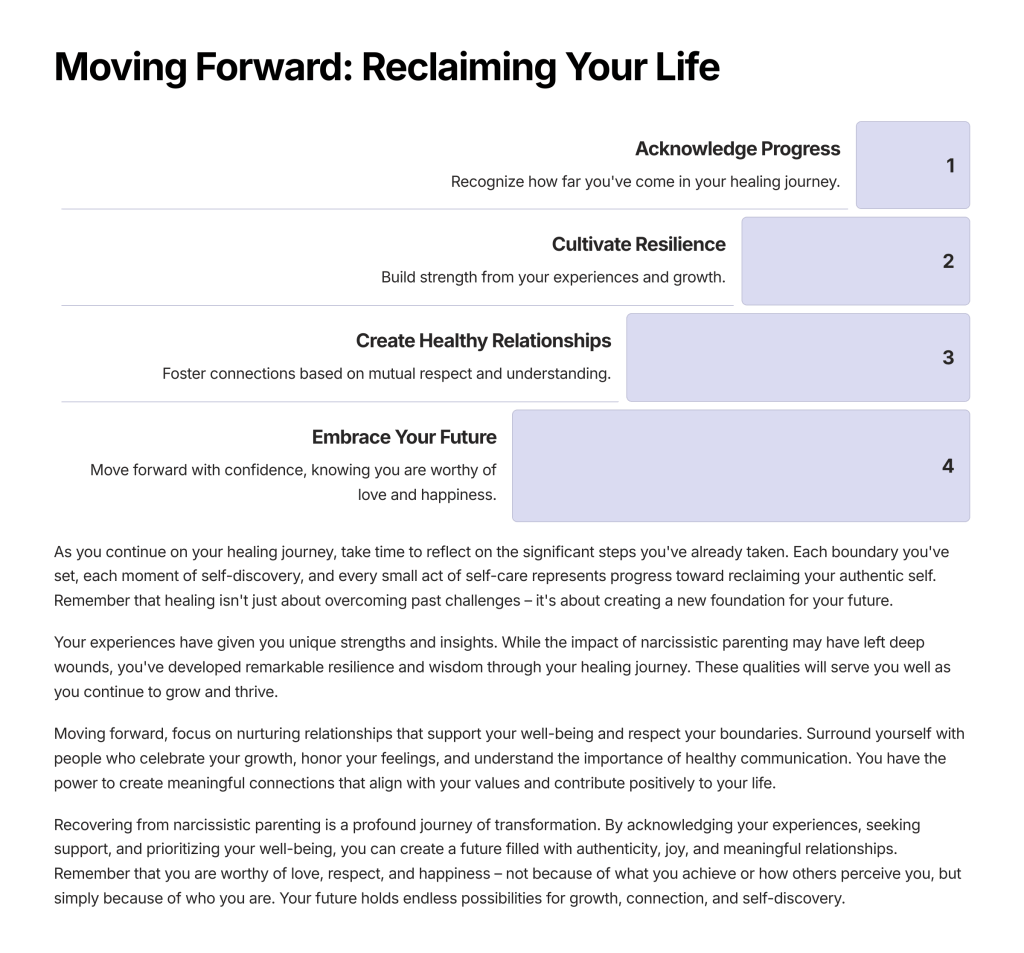
Processing emotions and working through discomfort isn’t about reaching a state where you never feel bad again. It’s about developing the capacity to live more fully in each moment, experiencing your feelings in real-time rather than carrying around emotional baggage from the past or anxiety about the future.
When you can look directly at what’s bothering you—when you can sit with discomfort long enough to understand its message—you begin to access parts of yourself that may have been hidden for years. You discover that beneath all the protective layers you’ve built up, your authentic self has been there all along, waiting to be acknowledged and expressed.
This process isn’t always comfortable, but it leads to something invaluable: the freedom to respond to life from a place of choice rather than reaction, to make decisions based on who you actually are rather than who you think you should be, and to experience the full range of human emotion without being overwhelmed by it.
Your discomfort has been trying to tell you something important. Maybe it’s time to finally listen.